Gas prices are rising again amid global uncertainty caused by the Trump administration's trade tariffs and restrictions against several countries, including Mexico and Canada. These measures have been postponed for a month to allow for trade negotiations.
According to the latest data, global LNG trade in 2024 grew to 407 million tons, up from 404 million tons the previous year, marking the slowest growth in a decade.

Several factors contributed to this slowdown, including rising gas prices, economic instability in key importing countries, and increased domestic gas production in some regions. Nevertheless, LNG remains a crucial energy source, particularly for countries lacking natural gas reserves.
Economists predict that LNG demand will continue to grow in the coming years, but at a more moderate pace. The key drivers shaping the market will be the development of infrastructure for LNG import and regasification, as well as government energy policies. Special attention will be given to projects aimed at reducing greenhouse gas emissions during LNG production and transportation.
For example, in 2024, Europe reduced LNG imports by 23 million tons, but in 2025, its demand is expected to rise again. Experts believe that Europe will compete with Asia for LNG supplies to replenish stocks ahead of winter, as new LNG production capacity will only come online in the second half of the year.
This competition will intensify due to declining domestic gas production in Europe and limited pipeline supply expansion. European countries will have to seek alternative energy sources, such as renewables and coal, to offset the gas shortage. However, these alternatives have their limitations and may hinder Europe's climate goals. The impact on global LNG prices will also be significant. Prices are expected to rise during peak demand periods, leading to higher costs for consumers and industries.
As for China, the country imported 79 million tons of LNG in 2024, nearly reaching its 2021 peak. This impressive volume reflects China's growing need for clean energy and its efforts to diversify energy sources. The rapid economic recovery has driven LNG demand across industries, power generation, and residential heating. Increased LNG imports also align with China's policies aimed at reducing carbon emissions and improving air quality. Since LNG is a cleaner alternative to coal, it remains an attractive option to meet the country's rising energy demands.
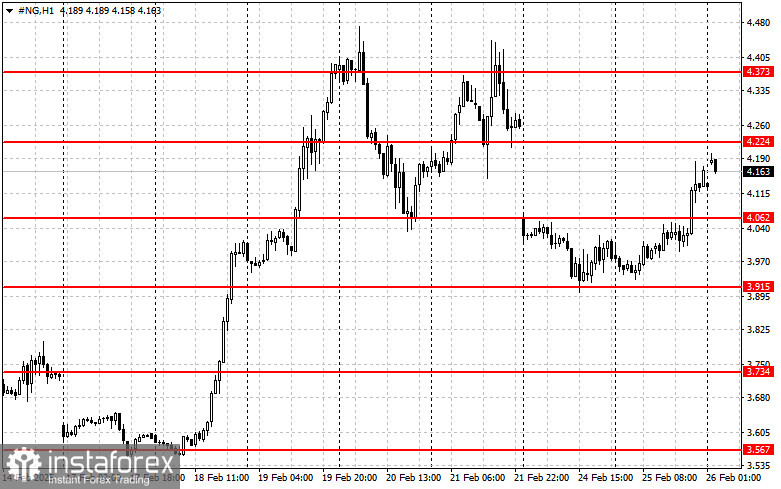
Technical Analysis of NG
For buyers, the key challenge is reclaiming the 4.224 level. A breakout above this range would pave the way toward 4.373, followed by a stronger resistance at 4.490, with the final target at 4.510.
In case of further declines, the first support level is around 4.062. A drop below this mark could quickly push the asset down to 3.915, with the lowest target at 3.734.
 English
English 
 Русский
Русский Bahasa Indonesia
Bahasa Indonesia Bahasa Malay
Bahasa Malay ไทย
ไทย Español
Español Deutsch
Deutsch Български
Български Français
Français Tiếng Việt
Tiếng Việt 中文
中文 বাংলা
বাংলা हिन्दी
हिन्दी Čeština
Čeština Українська
Українська Română
Română

