
1. Misinformation
The development of technology, especially artificial intelligence, has made it easier to create and spread misinformation, leading to a rise in fabricated content and "synthetic" news. This creates a fertile ground for manipulating public opinion and destabilizing society.
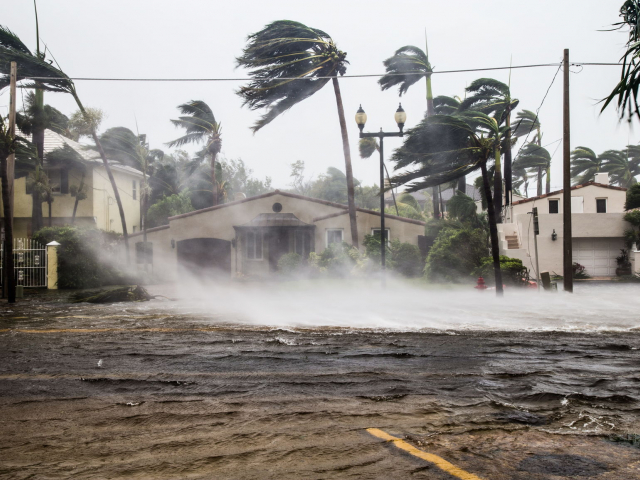

2. Extreme weather events
Due to climate change, the world is increasingly facing natural disasters such as extreme heatwaves, floods, and hurricanes. These events cause significant damage to the economy, infrastructure, and public health. For instance, in 2023, economic losses from natural disasters exceeded $200 billion.

3. Armed conflicts between nations
Twenty-three percent of World Economic Forum experts believe that armed conflicts will be the biggest threat to the global economy in the near future. The escalation of geopolitical tensions could lead to rising energy and commodity prices, supply chain disruptions, increased sanctions, and slower investment, triggering inflation and a global economic downturn.
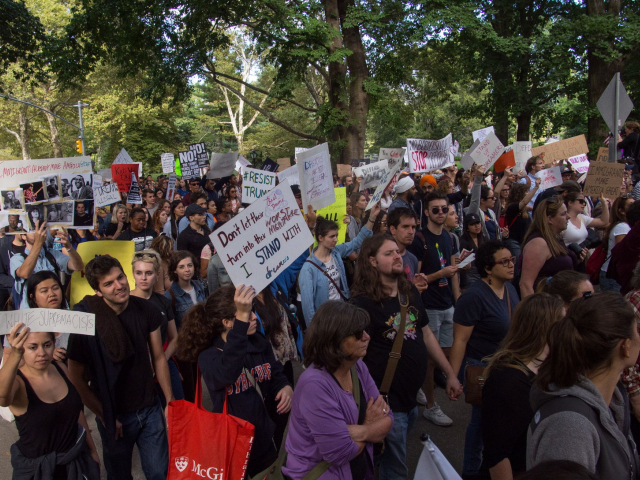
4. Societal polarization
Society is increasingly divided into opposing camps based on political, social, and cultural views. Polarization hinders dialogue, heightens hostility, and fuels radical sentiments. According to research, in 2023, trust in government institutions fell in 24 out of 28 major countries worldwide.
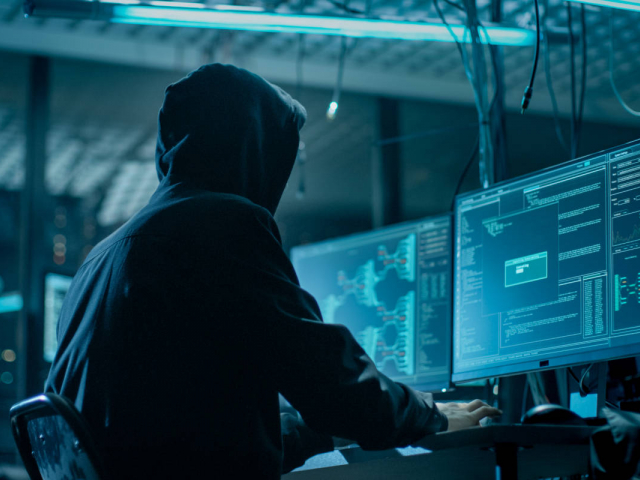

5. Cybercrime
As dependence on digital technologies grows, so does the risk of cyberattacks. Cyber espionage and cyber warfare could disrupt critical infrastructure and cause significant economic damage. IBM experts predict that global losses from cybercrime could exceed $10.5 trillion by 2025, making it one of the most costly threats to the global economy.
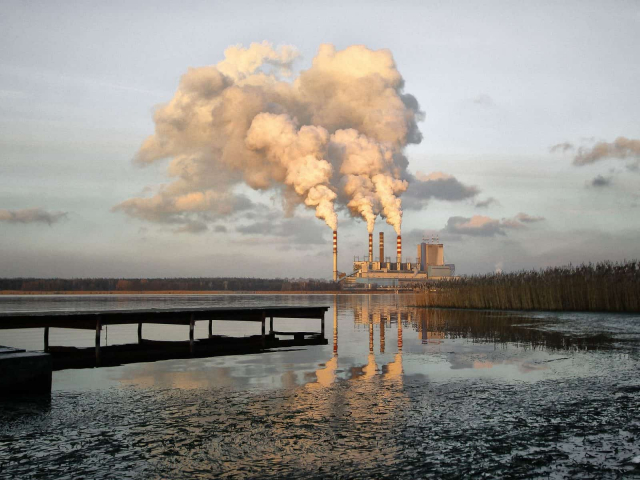

6. Environmental pollution
Ongoing environmental pollution causes immense harm to ecosystems and human health. About 7 million people die annually from diseases related to air pollution. Plastic waste in the oceans destroys marine ecosystems and threatens food security. Soil pollution is equally dangerous: according to the UN, around 33% of the world's land has already degraded due to chemical waste, pesticides, and unsustainable agriculture.
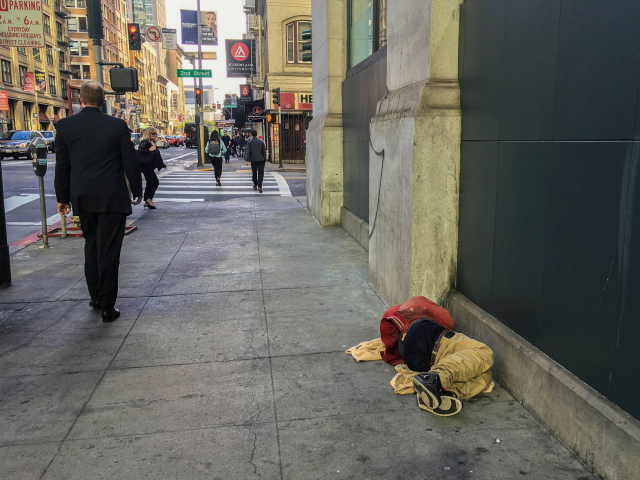

7. Inequality
A widening gap between the rich and the poor exacerbates social tensions and hinders sustainable development. Economic inequality limits access to education, healthcare, and other basic services for a large portion of the population, slowing overall progress and potentially leading to social unrest.
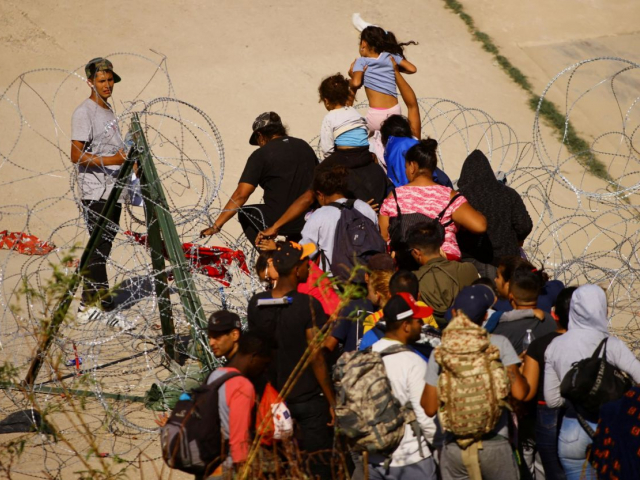

8. Forced migration
Conflicts, economic crises, and climate change are forcing millions of people to leave their homes. According to the UN, the number of displaced people reached a record 100 million in 2023. Mass migration puts pressure on host countries, creating social and economic challenges and fueling xenophobic sentiments.
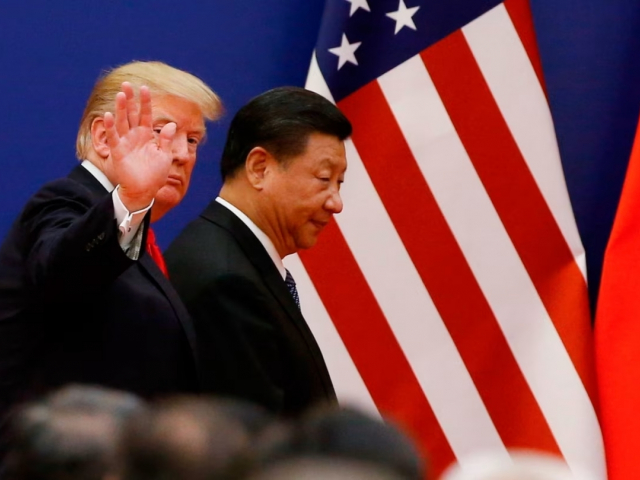

9. Geo-economic confrontation
Increased economic competition between countries, manifested in trade wars, sanctions, and protectionist measures, destabilizes global markets. Such confrontations disrupt supply chains, increase the cost of goods and services, and slow economic growth. For example, trade disputes between the United States and China have caused significant volatility in global markets in recent years.
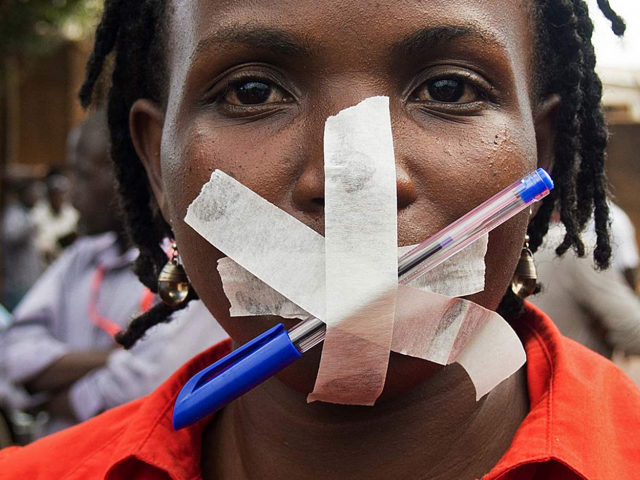

10. Erosion of human rights and civil liberties
In some regions, there are restrictions on basic rights and freedoms such as freedom of speech, assembly, and the press. This undermines democratic values and can lead to authoritarianism. International organizations report an increase in the persecution of journalists, activists, and minorities, calling for stronger measures to protect human rights worldwide.
 English
English 
 Русский
Русский Bahasa Indonesia
Bahasa Indonesia Bahasa Malay
Bahasa Malay ไทย
ไทย Español
Español Deutsch
Deutsch Български
Български Français
Français Tiếng Việt
Tiếng Việt 中文
中文 বাংলা
বাংলা हिन्दी
हिन्दी Čeština
Čeština Українська
Українська Română
Română
